binary, the belief that there are only two distinct and opposite categories
gender nonconforming, an individual whose behavior and/or gender expression do not conform to society’s norms for masculine and feminine.
masculinity, traditional behaviors and traits associated with men (HP), and femininity, traditional behaviors, and traits associated with women,
feminine-expressive role, providing care and emotional support,
masculine-instrumental role, goal-oriented and providing financial support
intersex, a person born with variations in male and female hormones, chromosomes, and/or sexual organs
gender identity, an individual’s inner sense, and identification of being masculine or feminine,
| Gender Nonconformity | An individual whose behavior and/or gender expression does not conform to society’s norms for masculine and feminine. |
| Genderqueer | A person whose gender expression and/or identity is neither masculine nor feminine. Genderqueer is sometimes used synonymously with non-binary or gender fluid. |
| Cisgender | An individual whose gender identity matches their sex at birth. |
| Transgender | A person who identifies with a gender that is different from their biological sex. |
gender norms, behaviors, or traits that society attributes to a particular sex
gender roles, public expression of one’s gender identity
- Gender is not only related to what a person is but what a person does in social interactions.
- We do gender knowing others will judge our performance, especially if we do gender outside the normative gender scripts.
- Children are taught from an early age about doing gender and monitoring their own behavior and their peers to ensure their behavior is gender appropriate.
sexism, prejudice, devaluation, and discrimination based on an individual’s sex
Male characters are typically portrayed in the media as
- active, powerful, and adventurous
- sexually aggressive
- largely uninvolved in human relationships
Females characters are typically portrayed in media as
- young, thin, and beautiful
- passive, dependent, and often incompetent
- devoted to improving their appearance
At ages 2–6, kids
- learn their gender identities (that they’re a boy or a girl)
- learn stereotypes about activities, traits, toys, and skills associated with each gender
- begin gender-typed play (girls shop, dress up, and play “mom” with baby dolls while boys play racetrack cars, Legos, and sports)
- need to hear your input in specific, not abstract, terms
What you can do
- point out people from real life or TV that show more than one way to do gender
- comment positively on shows that equally value boys and girls
- find shows that aren’t hyper-pink or super-blue
- Parents dress infants based on sex, provide sex-specific toys, and expect different behavior from boys and girls (Thorne 1993).
- Two-and-a-half-year-olds use gender stereotypes derived from parents to understand their world (Fagot, Leinbach, and O’Boyle 1992).
- Parents encourage their children to participate in sex-typed activities (Rocha 2005).
- Parents’ assignment of gender-specific chores links certain types of work with gender (Wood 2012)
second shift, the unpaid childcare and household responsibilities completed by women that are in addition to their paid work in the labor force.

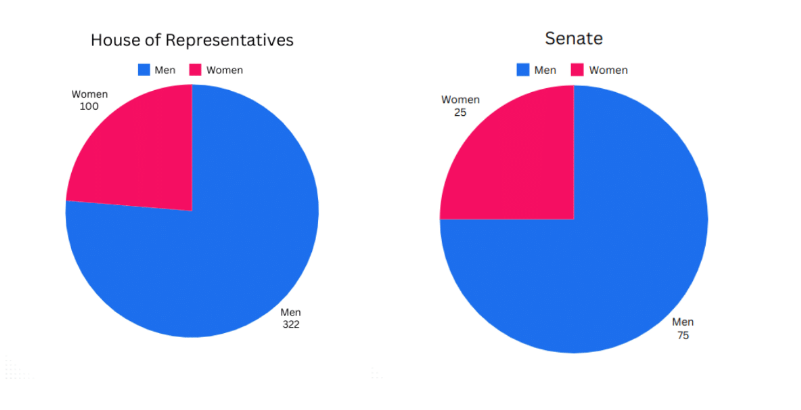
Gender stratification, the unequal access and distribution of wealth, power, and privilege between women and men
glass escalator, which means that men in female-dominated careers rise faster than women in male-dominated careers 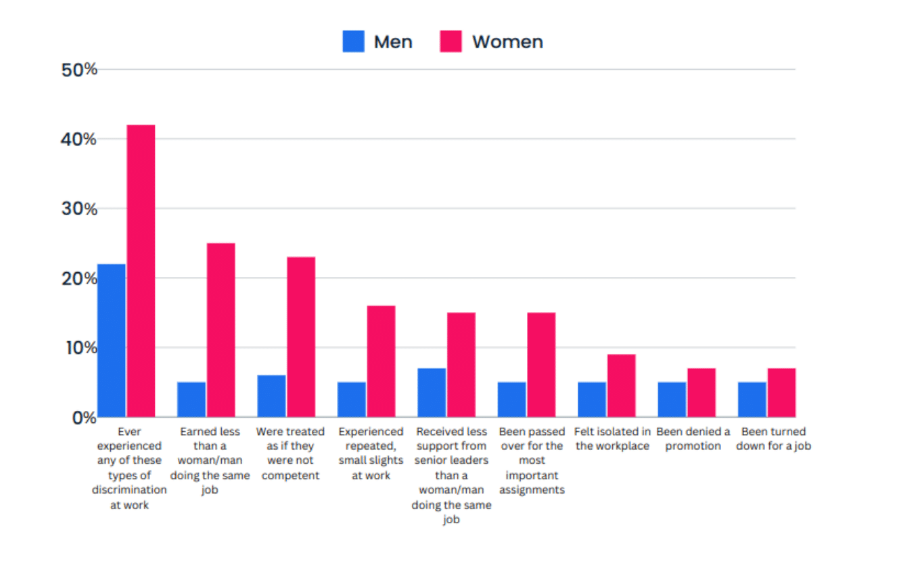
glass escalator, which means that men in female-dominated careers rise faster than women in male-dominated careers
glass ceiling, social and legal barriers designed to prevent minorities and women from advancing in the workplace
Structural barriers related to gender
- unequal educational opportunities and attainment
- conscious and unconscious stereotyping, prejudice, and bias
- lack of vigorous, consistent government monitoring and law enforcement
Corporate barriers related to gender
- climates that alienate and isolate women
- special or different standards for performance evaluation
- counterproductive behavior and harassment by colleagues
Sexual harassment, unwelcome sexual advances, requests for sexual favors, and other verbal and physical harassment of a sexual nature (HP), is one of the most discussed topics in employee relations today. It is divided into two types; quid pro quo, express or implied demands by an employer or supervisor for sexual favors in exchange for some benefit such as a promotion, raise, or preferential treatment (C-19), and a hostile environment, an intimidating, hostile, or offensive working environment due to unwelcome verbal or physical conduct of a sexual nature (U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission 2012; Crucet et al. 2010).
intersectionality, the overlap of personal and social identities that manifests as disadvantage and discrimination in people’s lives
|
U.S. College Degrees by Gender |
|||||||
| Degrees |
Class of 2017 |
Class of 2026 (estimated) |
|||||
| Percentages | Females per 100 Males | Percentages | Females per 100 Males | ||||
| Male | Female | Male | Female | ||||
| Associate’s | 37.9% | 62.1% | 164 | 34.9% | 65.1% | 187 | |
| Bachelor’s | 42.9% | 57.3% | 134 | 41.8% | 58.2% | 139 | |
| Master’s | 41.7% | 58.3% | 140 | 41.6% | 58.4% | 140 | |
| Doctoral’s | 47.8% | 52.2% | 109 | 47.6% | 52.4% | 110 | |
| All Degrees | 41.5% | 58.5% | 141 | 40.0% | 60.0% | 150 | |
honor killing, the killing of a female family member for the perceived shame she has brought onto the family,
violence against women, any act that results in the mental, physical and/or sexual harm of a girl, teen, or woman
| Social Learning Theory | Individuals who witness or experience violence while growing up are likelier to use violence as adults. |
| Social Situation or Stress Theory | Violence is greatly influenced by the stress in a particular situation that may be part of the larger society or specific to a particular group. Also, culture may work to normalize violence in society. |
| Resource Theory | One perspective on this theory states that the more resources an individual has, the more control and force he can apply in the relationship. On the other hand, some contend that the fewer resources a person has, the more likely he is to compensate by resorting to violence. |
| Exchange Theory | Based on the economic principles of costs and benefits, this theory contends that an abuser will use violence when the benefits exceed the costs. |
| Feminist Theory | Looks at the history of male domination in societies worldwide and contends that larger social and economic processes work to subordinate women in society and the home. |
| General Systems Theory | The violence experienced by women isn’t just about the individual abuser but about the family systems or structure overall, which is made up of multiple people that play varying roles that are changeable over time. |

- Making them afraid by using looks, actions, and/or gestures
- Smashing things
- Destroying their property
- Abusing pets
- Displaying weapons
- Putting them down
- Making them feel bad about themselves
- Calling them names
- Making them think they’re crazy
- Making them feel guilty
- Controlling what they do, who they see and talk to, what they read, and where they go
- Limiting their outside involvement
- Using jealousy to justify actions
- Making light of the abuse and not taking their concerns about it seriously
- Saying the abuse didn’t happen
- Shifting responsibility for abusive behavior
- Saying they caused it
- Making them feel guilty about the children
- Using the children to relay messages
- Using visitation to harass them
- Threatening to take the children away
- Treating them like a servant
- Making all the big decisions
- Acting as the master of the castle
- Being the one to define the relationship roles
- Preventing them from getting or keeping a job
- Making them ask for money
- Giving them an allowance
- Taking their money
- Not letting them know about or have access to the family income
- Making and/or carrying out threats to do something to hurt them
- Threatening to leave them, commit suicide, or report them to welfare
- Making them drop charges
- Making them do illegal things
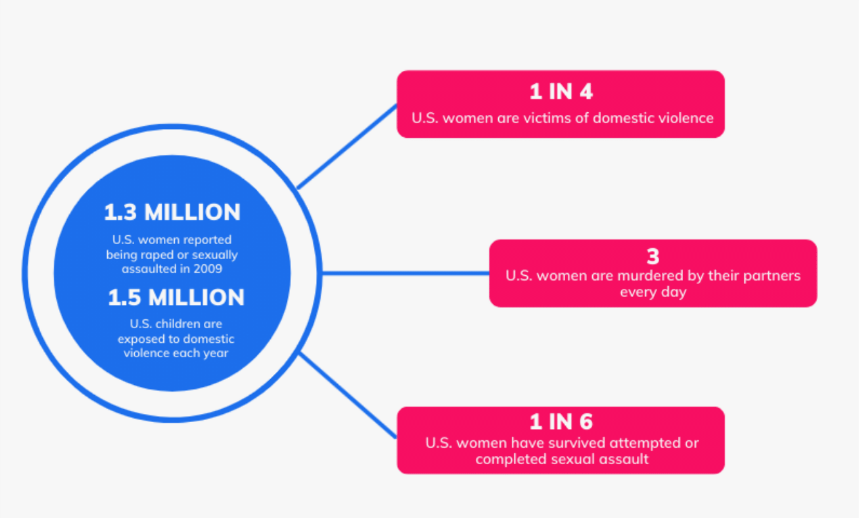
Violence Against Women Act (VAWA). VAWA legislation contained a few key provisions designed to improve society’s response to violence against women:
- requiring that orders of protection be honored throughout the nation
- mandating that rape victims not have to pay for the cost of their rape exam and creating rape shield laws that prevent a woman’s past sexual conduct from being used against her in court
- increasing training for law enforcement officials and members of the criminal justice system regarding the realities of violence against women
- distributing grant money to many of the nation’s programs to prevent violence against women
(White House 2013)
The Violence Against Women Act was signed into law in 1994.
microaggressions, words, and deeds that negatively impact marginalized individuals, groups, or communities
| Microassaults |
Derogatory comments or actions |
| Microinsults | Snubs and hidden insults |
| Microinvalidations | An attempt to negate the feelings and experiences of others |
| Sexuality | Sexuality is similar to but different from the term “sex.” Therefore, “sex and gender” and “sexuality and gender” represent two distinct concepts. Sex is biological, while gender is a social construction. Instead of being strictly about biology, sexuality refers to the expression of the individual’s behaviors and desires. |
| Sexual Orientation | An individual’s sexual interest toward the same, opposite, neither, or both sexes. Sexual orientation is a means of expressing oneself as a sexual being. |
| Heterosexual | Individuals with a sexual interest in the opposite sex. |
| Homosexual | Individuals with a sexual interest in the same sex. |
| Bisexual | Individuals with a sexual interest in both sexes. |
| Asexual | Individuals who are not sexually attracted to others. |
| Pansexual | Individuals who are attracted to all people regardless of their gender identity or sexuality. This attraction can be emotional, romantic, and/or sexual. |
hookups, a sexual encounter, usually lasting only one night, between two individuals who are strangers or brief acquaintances
queer theory, a perspective that emerged in the 1990s, challenging the normative assumptions of heterosexuality and homosexuality